Initial Query
Draw an image of a triangle using WebGL in a single HTML file. Make the canvas take the full page.
LLM Generation
Query
Draw an image of a triangle using WebGL in a single HTML file. Make the canvas take the full page.
Output
Below is a complete HTML file that creates a full-page WebGL canvas and draws a red triangle:
--------------------------------------------------
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>WebGL Triangle</title>
<style>
/* Remove default margins and ensure body and canvas take the full window */
html,
body,
canvas {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: block;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="glcanvas"></canvas>
<script>
// Get the canvas and initialize the WebGL context.
const canvas = document.getElementById("glcanvas");
const gl =
canvas.getContext("webgl") || canvas.getContext("experimental-webgl");
if (!gl) {
alert("WebGL isn't available in your browser.");
}
// Resize the canvas to fill the window.
function resizeCanvas() {
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);
}
window.addEventListener("resize", resizeCanvas);
resizeCanvas();
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec2 aVertexPosition;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = vec4(aVertexPosition, 0.0, 1.0);
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // red
}
`;
// A helper function to compile a shader.
function loadShader(type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
gl.compileShader(shader);
// Check if compiled successfully.
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
alert("An error occurred compiling the shaders: " + gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader));
gl.deleteShader(shader);
return null;
}
return shader;
}
// Compile the shaders.
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vsSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fsSource);
// Create the shader program.
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check if the program linked successfully.
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
alert("Unable to initialize the shader program: " + gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram));
}
// Locate the attribute in the shader program.
const vertexPositionAttribute = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, "aVertexPosition");
// Set up the vertices for a triangle.
const vertices = new Float32Array([
0.0, 0.5, // top vertex
-0.5, -0.5, // bottom left vertex
0.5, -0.5, // bottom right vertex
]);
// Create a buffer and load the vertex data into it.
const vertexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Draw the scene.
function drawScene() {
// Clear the canvas with a black color.
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Use our shader program.
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// Bind the vertex buffer.
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vertexPositionAttribute);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(vertexPositionAttribute, 2, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0);
// Draw the triangle.
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
}
drawScene();
</script>
</body>
</html>
--------------------------------------------------
Instructions:
1. Save the code above into a file (for example, triangle.html).
2. Open the file in your browser.
3. The canvas will cover the full page and display a red triangle on a black background.
This file is self-contained and uses WebGL to draw a triangle with no external dependencies. Enjoy!
Extract Code
I extracted the following code from that output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122 | <!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>WebGL Triangle</title>
<style>
/* Remove default margins and ensure body and canvas take the full window */
html,
body,
canvas {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
display: block;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="glcanvas"></canvas>
<script>
// Get the canvas and initialize the WebGL context.
const canvas = document.getElementById("glcanvas");
const gl =
canvas.getContext("webgl") || canvas.getContext("experimental-webgl");
if (!gl) {
alert("WebGL isn't available in your browser.");
}
// Resize the canvas to fill the window.
function resizeCanvas() {
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);
}
window.addEventListener("resize", resizeCanvas);
resizeCanvas();
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec2 aVertexPosition;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = vec4(aVertexPosition, 0.0, 1.0);
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // red
}
`;
// A helper function to compile a shader.
function loadShader(type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
gl.compileShader(shader);
// Check if compiled successfully.
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
alert("An error occurred compiling the shaders: " + gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader));
gl.deleteShader(shader);
return null;
}
return shader;
}
// Compile the shaders.
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vsSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fsSource);
// Create the shader program.
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check if the program linked successfully.
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
alert("Unable to initialize the shader program: " + gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram));
}
// Locate the attribute in the shader program.
const vertexPositionAttribute = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, "aVertexPosition");
// Set up the vertices for a triangle.
const vertices = new Float32Array([
0.0, 0.5, // top vertex
-0.5, -0.5, // bottom left vertex
0.5, -0.5, // bottom right vertex
]);
// Create a buffer and load the vertex data into it.
const vertexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Draw the scene.
function drawScene() {
// Clear the canvas with a black color.
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Use our shader program.
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// Bind the vertex buffer.
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vertexPositionAttribute);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(vertexPositionAttribute, 2, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0);
// Draw the triangle.
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
}
drawScene();
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Check if all of the following conditions are true:
HTML Render
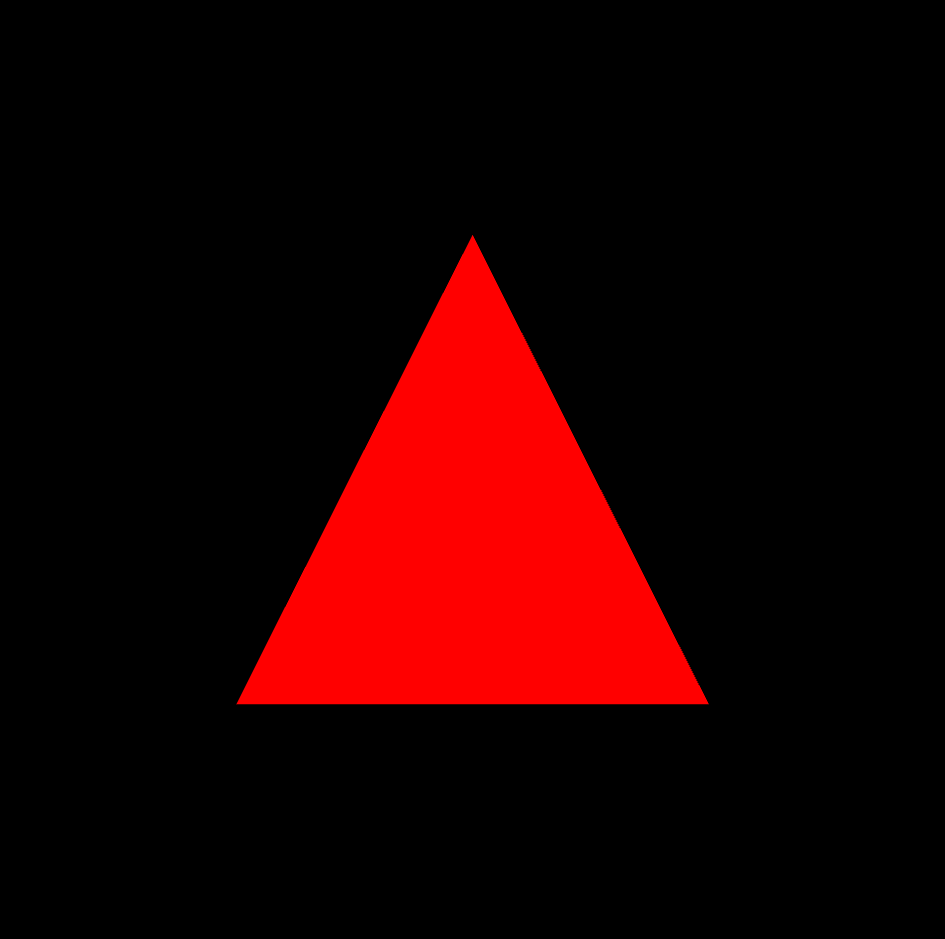
Rendering the webpage gives the following image:
LLM Generation
Query
This is a screenshot of a webpage that draws something with webgl. I'm trying to see if it drew what I wanted. Describe what is drawn in this image?
Output
The image shows a red triangle centered on a black background.
LLM Generation
Query
Does this answer say that there is a picture of a triangle "The image shows a red triangle centered on a black background."? Answer "Yes it does" or "No it does not".
Output
Yes it does.
Substring Evaluation
Testing if the previous output contains the string es it does: True
Check this condition is not true:
Substring Evaluation
Testing if the previous output contains the string THREE.: False
Final Answer: True
Final Answer: True
Initial Query
Draw an image of a triangle using WebGL in a single HTML file. Make the canvas take the full page.
LLM Generation
Query
Draw an image of a triangle using WebGL in a single HTML file. Make the canvas take the full page.
Output
Below is a complete HTML file that uses WebGL to draw a triangle and makes the canvas take up the full page.
------------------------------------------------------------
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>WebGL Triangle Full Page</title>
<style>
/* Remove default margin/padding and make canvas fill the viewport */
html,
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
canvas {
display: block;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="glcanvas"></canvas>
<script>
// Get canvas and setup WebGL context
const canvas = document.getElementById('glcanvas');
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
// Resize canvas to full viewport size
function resizeCanvas() {
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
// Update the viewport with the canvas size
gl.viewport(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
}
window.addEventListener('resize', resizeCanvas);
resizeCanvas();
if (!gl) {
alert('Unable to initialize WebGL. Your browser or machine may not support it.');
}
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec2 aPosition;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = vec4(aPosition, 0.0, 1.0);
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
// Set the fragment color to blue
gl_FragColor = vec4(0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0);
}
`;
// Initialize a shader program
function initShaderProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource) {
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl, gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vsSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl, gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fsSource);
// Create the shader program
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check for errors
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
alert('Unable to initialize the shader program: ' + gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram));
return null;
}
return shaderProgram;
}
// Create a shader from source code
function loadShader(gl, type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
gl.compileShader(shader);
// Check for compile errors
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
alert('An error occurred compiling the shaders: ' + gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader));
gl.deleteShader(shader);
return null;
}
return shader;
}
// Initialize the shader program
const shaderProgram = initShaderProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource);
// Collect attribute locations
const attribLocations = {
vertexPosition: gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aPosition'),
};
// Define the positions for a triangle (covering a central region)
const positions = new Float32Array([
0.0, 0.8, // Top vertex
-0.8, -0.8, // Bottom left vertex
0.8, -0.8 // Bottom right vertex
]);
// Create a buffer for triangle's positions
const positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positions, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Draw the scene
function drawScene() {
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // Clear to black
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Tell WebGL to use our shader program
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// Enable the vertex attribute array and bind the buffer
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(attribLocations.vertexPosition);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
attribLocations.vertexPosition,
2, // 2 components per iteration (x, y)
gl.FLOAT, // Data type
false, // Normalize
0, // Stride (0 = auto)
0 // Offset
);
// Draw the triangle (3 vertices)
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
}
// Draw the scene for the first time.
drawScene();
</script>
</body>
</html>
------------------------------------------------------------
Explanation:
1. The CSS in the style block removes default margins and sets the canvas to fill the entire viewport.
2. The JavaScript obtains the WebGL context and sets up the viewport to match the canvas size.
3. Two shader programs (vertex and fragment) are defined:
• The vertex shader receives a 2D position and converts it to clip space.
• The fragment shader colors the triangle blue.
4. A triangle is defined with three 2D vertices.
5. The drawScene() function clears the canvas and draws the triangle.
Open this file in a WebGL-capable browser to see your full-page triangle!
Extract Code
I extracted the following code from that output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142 | <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>WebGL Triangle Full Page</title>
<style>
/* Remove default margin/padding and make canvas fill the viewport */
html,
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
canvas {
display: block;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="glcanvas"></canvas>
<script>
// Get canvas and setup WebGL context
const canvas = document.getElementById('glcanvas');
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
// Resize canvas to full viewport size
function resizeCanvas() {
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
// Update the viewport with the canvas size
gl.viewport(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
}
window.addEventListener('resize', resizeCanvas);
resizeCanvas();
if (!gl) {
alert('Unable to initialize WebGL. Your browser or machine may not support it.');
}
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec2 aPosition;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = vec4(aPosition, 0.0, 1.0);
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
// Set the fragment color to blue
gl_FragColor = vec4(0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0);
}
`;
// Initialize a shader program
function initShaderProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource) {
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl, gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vsSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl, gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fsSource);
// Create the shader program
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check for errors
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
alert('Unable to initialize the shader program: ' + gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram));
return null;
}
return shaderProgram;
}
// Create a shader from source code
function loadShader(gl, type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
gl.compileShader(shader);
// Check for compile errors
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
alert('An error occurred compiling the shaders: ' + gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader));
gl.deleteShader(shader);
return null;
}
return shader;
}
// Initialize the shader program
const shaderProgram = initShaderProgram(gl, vsSource, fsSource);
// Collect attribute locations
const attribLocations = {
vertexPosition: gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aPosition'),
};
// Define the positions for a triangle (covering a central region)
const positions = new Float32Array([
0.0, 0.8, // Top vertex
-0.8, -0.8, // Bottom left vertex
0.8, -0.8 // Bottom right vertex
]);
// Create a buffer for triangle's positions
const positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positions, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Draw the scene
function drawScene() {
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // Clear to black
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Tell WebGL to use our shader program
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// Enable the vertex attribute array and bind the buffer
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(attribLocations.vertexPosition);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
attribLocations.vertexPosition,
2, // 2 components per iteration (x, y)
gl.FLOAT, // Data type
false, // Normalize
0, // Stride (0 = auto)
0 // Offset
);
// Draw the triangle (3 vertices)
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
}
// Draw the scene for the first time.
drawScene();
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Check if all of the following conditions are true:
HTML Render
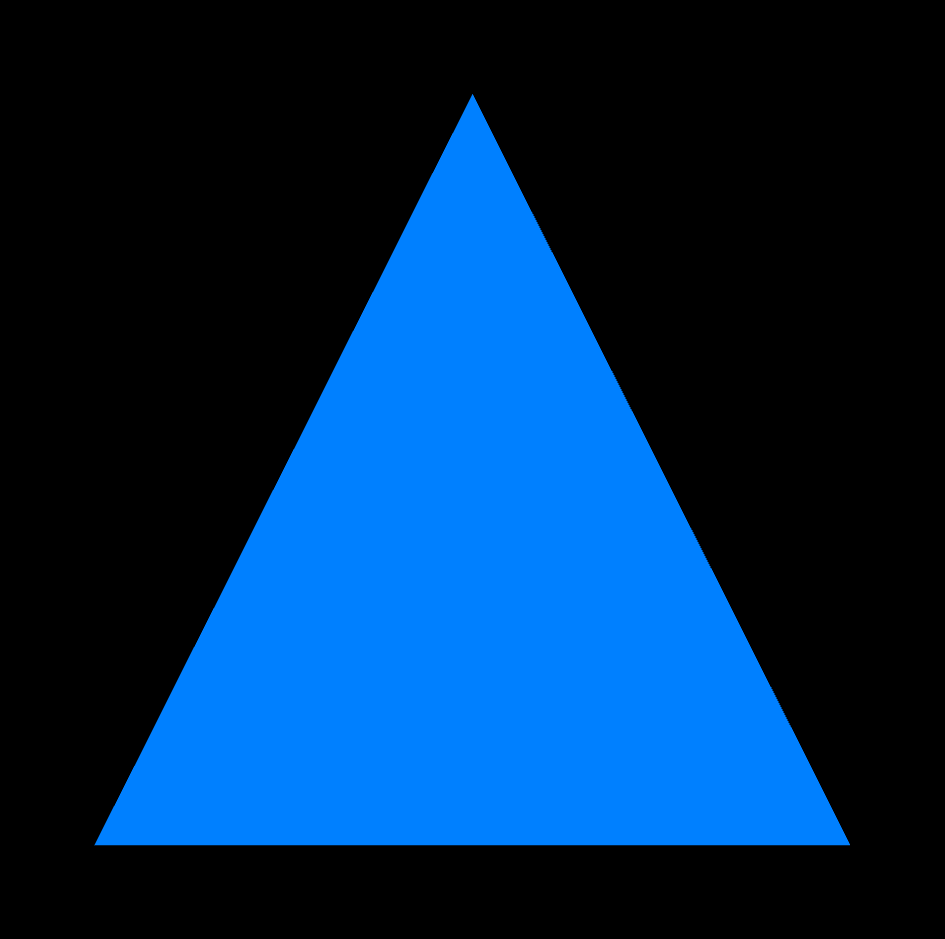
Rendering the webpage gives the following image:
LLM Generation
Query
This is a screenshot of a webpage that draws something with webgl. I'm trying to see if it drew what I wanted. Describe what is drawn in this image?
Output
The image shows a blue triangle centered on a black background.
LLM Generation
Query
Does this answer say that there is a picture of a triangle "The image shows a blue triangle centered on a black background."? Answer "Yes it does" or "No it does not".
Output
Yes it does.
Substring Evaluation
Testing if the previous output contains the string es it does: True
Check this condition is not true:
Substring Evaluation
Testing if the previous output contains the string THREE.: False
Final Answer: True
Final Answer: True

