Initial Query
Draw an image of a triangle using WebGL in a single HTML file. Make the canvas take the full page.
LLM Generation
Query
Draw an image of a triangle using WebGL in a single HTML file. Make the canvas take the full page.
Output
Certainly! Below is a complete HTML file that uses WebGL to draw a simple colored triangle. The canvas is set to take up the full browser window.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130 | <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>WebGL Full Page Triangle</title>
<style>
/* Remove default margins and ensure the canvas covers the full page */
body, html {
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
canvas {
display: block; /* Removes the small space below the canvas */
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- The canvas element where WebGL will draw -->
<canvas id="glcanvas"></canvas>
<script type="text/javascript">
// Get the canvas element
const canvas = document.getElementById('glcanvas');
// Initialize the WebGL context
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
if (!gl) {
alert('Unable to initialize WebGL. Your browser may not support it.');
throw new Error('WebGL not supported');
}
// Set the viewport to match the canvas size
function resizeCanvas() {
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);
}
// Resize the canvas to fit the window
window.addEventListener('resize', resizeCanvas);
resizeCanvas();
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec4 aVertexPosition;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = aVertexPosition;
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vec4(0.0, 0.6, 1.0, 1.0); // Light blue color
}
`;
// Compile shader and check for errors
function loadShader(type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
gl.compileShader(shader);
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
const info = gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader);
gl.deleteShader(shader);
throw new Error('An error occurred compiling the shaders: ' + info);
}
return shader;
}
// Initialize shaders
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vsSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fsSource);
// Create the shader program
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check if the program was linked successfully
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
const info = gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram);
throw new Error('Unable to initialize the shader program: ' + info);
}
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// Define the positions for the triangle vertices
const vertices = new Float32Array([
0.0, 1.0, // Top vertex
-1.0, -1.0, // Bottom left vertex
1.0, -1.0 // Bottom right vertex
]);
// Create a buffer and bind the vertices
const vertexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Get the location of the attribute in the shader program
const vertexPosition = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aVertexPosition');
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vertexPosition);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
vertexPosition,
2, // Number of components per vertex (x, y)
gl.FLOAT, // Type of each component
false, // Normalize
0, // Stride (0 = auto)
0 // Offset from the beginning of buffer
);
// Set the clear color to black, fully opaque
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
// Clear the color buffer with specified clear color
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Draw the triangle
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
### Explanation of the Code:
1. **HTML & CSS Setup:**
- The `<canvas>` element with the ID `glcanvas` is where the WebGL content will be rendered.
- CSS is used to remove default margins and ensure the canvas occupies the entire browser window.
2. **Initializing WebGL:**
- The script starts by obtaining the WebGL rendering context from the canvas.
- A `resizeCanvas` function ensures that the canvas and WebGL viewport match the window size. It’s called initially and whenever the window is resized.
3. **Shaders:**
- **Vertex Shader (`vsSource`):** Processes each vertex's position.
- **Fragment Shader (`fsSource`):** Determines the color of each pixel. Here, it's set to a light blue color.
- The shaders are compiled and linked into a shader program that WebGL can use for rendering.
4. **Buffer Setup:**
- A buffer is created to store the triangle's vertex positions.
- The positions are defined in normalized device coordinates (ranging from -1 to 1 on both axes).
5. **Drawing the Triangle:**
- The canvas is cleared with a black color.
- The `gl.drawArrays` function is called with `gl.TRIANGLES` to render the three vertices as a single triangle.
### Running the Code:
1. **Save the Code:**
- Copy the entire code above into a file and save it with a `.html` extension, for example, `triangle.html`.
2. **Open in Browser:**
- Open the saved HTML file in a modern web browser (like Chrome, Firefox, or Edge) that supports WebGL.
3. **Result:**
- You should see a light blue triangle centered on a black background, with the canvas covering the entire browser window.
Feel free to modify the vertex positions or fragment shader to experiment with different triangle shapes and colors!
Extract Code
I extracted the following code from that output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130 | <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>WebGL Full Page Triangle</title>
<style>
/* Remove default margins and ensure the canvas covers the full page */
body, html {
margin: 0;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
canvas {
display: block; /* Removes the small space below the canvas */
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- The canvas element where WebGL will draw -->
<canvas id="glcanvas"></canvas>
<script type="text/javascript">
// Get the canvas element
const canvas = document.getElementById('glcanvas');
// Initialize the WebGL context
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
if (!gl) {
alert('Unable to initialize WebGL. Your browser may not support it.');
throw new Error('WebGL not supported');
}
// Set the viewport to match the canvas size
function resizeCanvas() {
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height);
}
// Resize the canvas to fit the window
window.addEventListener('resize', resizeCanvas);
resizeCanvas();
// Vertex shader program
const vsSource = `
attribute vec4 aVertexPosition;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = aVertexPosition;
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fsSource = `
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vec4(0.0, 0.6, 1.0, 1.0); // Light blue color
}
`;
// Compile shader and check for errors
function loadShader(type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
gl.compileShader(shader);
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
const info = gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader);
gl.deleteShader(shader);
throw new Error('An error occurred compiling the shaders: ' + info);
}
return shader;
}
// Initialize shaders
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vsSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fsSource);
// Create the shader program
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check if the program was linked successfully
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
const info = gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram);
throw new Error('Unable to initialize the shader program: ' + info);
}
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// Define the positions for the triangle vertices
const vertices = new Float32Array([
0.0, 1.0, // Top vertex
-1.0, -1.0, // Bottom left vertex
1.0, -1.0 // Bottom right vertex
]);
// Create a buffer and bind the vertices
const vertexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Get the location of the attribute in the shader program
const vertexPosition = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aVertexPosition');
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vertexPosition);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
vertexPosition,
2, // Number of components per vertex (x, y)
gl.FLOAT, // Type of each component
false, // Normalize
0, // Stride (0 = auto)
0 // Offset from the beginning of buffer
);
// Set the clear color to black, fully opaque
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
// Clear the color buffer with specified clear color
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Draw the triangle
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Check if all of the following conditions are true:
HTML Render
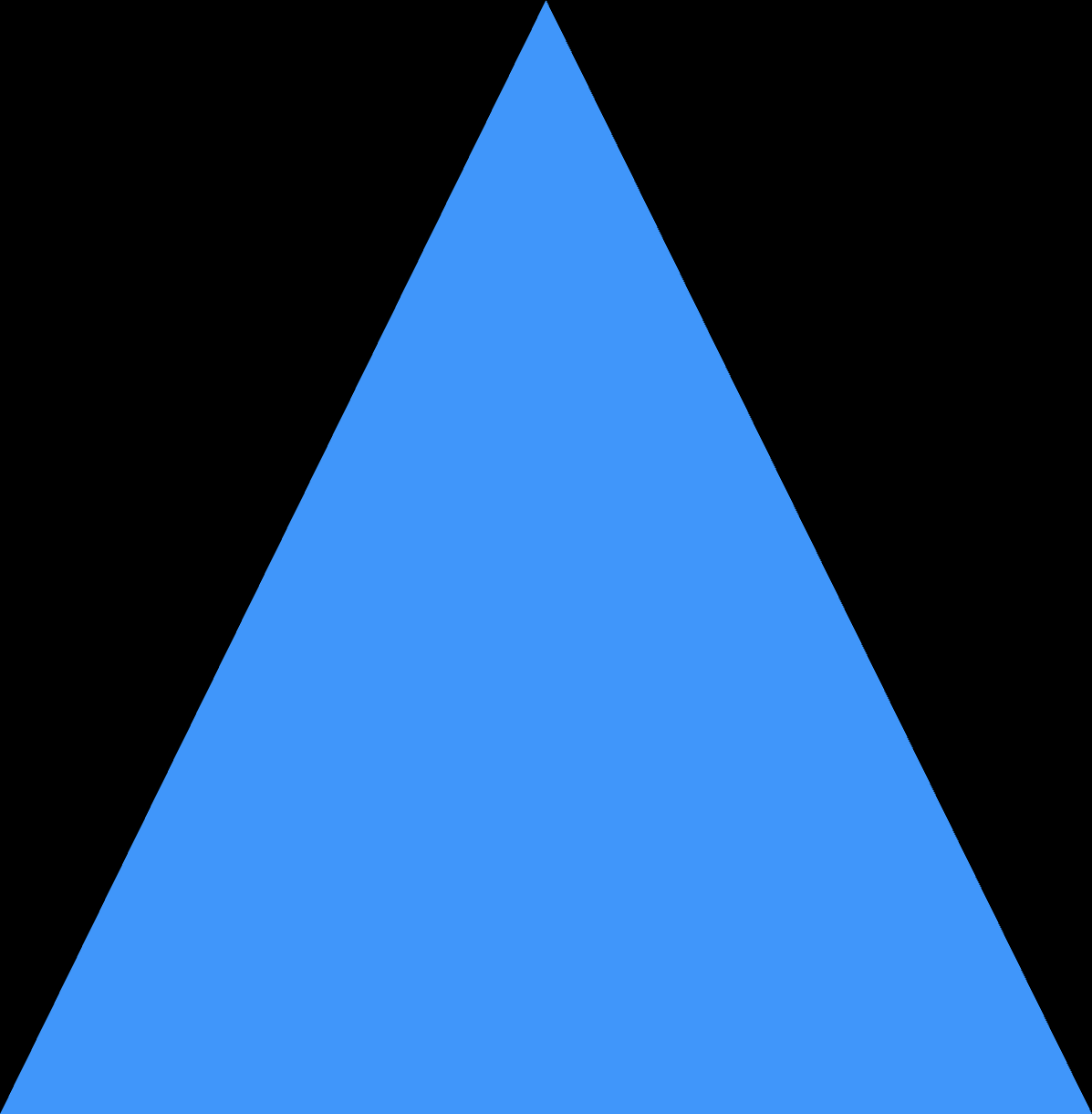
Rendering the webpage gives the following image:
LLM Generation
Query
This is a screenshot of a webpage that draws something with webgl. I'm trying to see if it drew what I wanted. Describe what is drawn in this image?
Output
The image shows a large blue triangle centered on a black background. The triangle's base spans the width of the image, and its apex points upwards, reaching near the top center of the image. The blue color of the triangle contrasts sharply with the black background.
LLM Generation
Query
Does this answer say that there is a picture of a triangle "The image shows a large blue triangle centered on a black background. The triangle's base spans the width of the image, and its apex points upwards, reaching near the top center of the image. The blue color of the triangle contrasts sharply with the black background."? Answer "Yes it does" or "No it does not".
Output
Yes it does.
Substring Evaluation
Testing if the previous output contains the string es it does: True
Check this condition is not true:
Substring Evaluation
Testing if the previous output contains the string THREE.: False
Final Answer: True
Final Answer: True
Initial Query
Draw an image of a triangle using WebGL in a single HTML file. Make the canvas take the full page.
LLM Generation
Query
Draw an image of a triangle using WebGL in a single HTML file. Make the canvas take the full page.
Output
Certainly! Below is a complete HTML file that uses WebGL to draw a simple colored triangle. The `<canvas>` element is styled to take up the full browser window.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153 | <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>WebGL Triangle</title>
<style>
/* Ensure the canvas fills the entire page */
html, body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
canvas {
display: block; /* Removes scrollbar in some browsers */
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Canvas element for WebGL rendering -->
<canvas id="glCanvas"></canvas>
<script>
// Get the canvas element
const canvas = document.getElementById('glCanvas');
// Initialize the WebGL context
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
if (!gl) {
alert('WebGL not supported, please use a different browser.');
}
// Vertex shader program
const vertexShaderSource = `
attribute vec4 aVertexPosition;
attribute vec4 aVertexColor;
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = aVertexPosition;
vColor = aVertexColor;
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fragmentShaderSource = `
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vColor;
}
`;
// Function to compile a shader
function loadShader(gl, type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
gl.compileShader(shader);
// Check if compiled successfully
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
const info = gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader);
gl.deleteShader(shader);
console.error('An error occurred compiling the shaders: ' + info);
return null;
}
return shader;
}
// Compile shaders
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl, gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vertexShaderSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl, gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fragmentShaderSource);
// Link the shaders into a program
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check if linking was successful
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
console.error('Unable to initialize the shader program: ' + gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram));
}
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// Get attribute locations
const vertexPosition = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aVertexPosition');
const vertexColor = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aVertexColor');
// Define the triangle's vertices and colors
const vertices = new Float32Array([
// X, Y, Z, R, G, B, A
0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, // Top vertex (red)
-1.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, // Bottom left vertex (green)
1.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0 // Bottom right vertex (blue)
]);
const FSIZE = vertices.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
// Create a buffer and bind the vertices
const vertexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Enable the vertex positions
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
vertexPosition,
3, // Number of components per vertex position
gl.FLOAT, // Data type
false, // Normalize
FSIZE * 7, // Stride (7 floats per vertex)
0 // Offset
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vertexPosition);
// Enable the vertex colors
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
vertexColor,
4, // Number of components per color
gl.FLOAT, // Data type
false, // Normalize
FSIZE * 7, // Stride (7 floats per vertex)
FSIZE * 3 // Offset (skip first 3 floats for position)
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vertexColor);
// Set the viewport to match the canvas size
function resizeCanvas() {
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.drawingBufferWidth, gl.drawingBufferHeight);
}
// Initial resize
resizeCanvas();
// Resize the canvas when the window is resized
window.addEventListener('resize', resizeCanvas);
// Clear the canvas with a black color
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Draw the triangle
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
### Explanation of the Code:
1. **HTML and CSS Setup**:
- The `<canvas>` element with the ID `glCanvas` is where the WebGL rendering occurs.
- CSS ensures that both the `html` and `body` elements, as well as the `canvas`, take up the full width and height of the viewport. This makes the canvas fill the entire page.
2. **WebGL Initialization**:
- The script retrieves the canvas and initializes the WebGL context.
- It defines vertex and fragment shader programs as strings. The vertex shader handles the position and color attributes, passing the color to the fragment shader.
- Shaders are compiled and linked into a shader program, which WebGL uses for rendering.
3. **Buffer Setup**:
- A buffer is created to store the triangle's vertices and their associated colors. Each vertex has seven components: three for position (`x`, `y`, `z`) and four for color (`r`, `g`, `b`, `a`).
- The buffer data is sent to the GPU, and the appropriate attributes are enabled and pointed to the correct locations within the buffer.
4. **Viewport and Resizing**:
- The `resizeCanvas` function ensures that the canvas and the WebGL viewport match the size of the browser window.
- An event listener updates the canvas size dynamically when the window is resized.
5. **Rendering**:
- The background is cleared with a black color using `gl.clearColor`.
- Finally, the triangle is drawn with `gl.drawArrays` using the `TRIANGLES` mode, specifying that three vertices should be used to form a single triangle.
### How to Use:
1. **Save the Code**:
- Copy the above HTML code into a text editor and save it with a `.html` extension, for example, `triangle.html`.
2. **Open in Browser**:
- Open the saved HTML file in a modern web browser that supports WebGL (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Edge).
3. **View the Triangle**:
- You should see a colored triangle (red, green, and blue vertices) centered on a black background, with the canvas filling the entire browser window.
### Additional Notes:
- **Colors**: Each vertex of the triangle has a distinct color. WebGL interpolates these colors across the surface of the triangle, creating a smooth gradient effect.
- **Responsive Design**: The canvas automatically resizes when the browser window size changes, ensuring the triangle remains properly scaled.
- **Error Handling**: Basic error handling is included to alert the user if WebGL is not supported by their browser.
Feel free to modify the vertex positions or colors to experiment with different triangle shapes and color schemes!
Extract Code
I extracted the following code from that output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153 | <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>WebGL Triangle</title>
<style>
/* Ensure the canvas fills the entire page */
html, body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
canvas {
display: block; /* Removes scrollbar in some browsers */
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Canvas element for WebGL rendering -->
<canvas id="glCanvas"></canvas>
<script>
// Get the canvas element
const canvas = document.getElementById('glCanvas');
// Initialize the WebGL context
const gl = canvas.getContext('webgl') || canvas.getContext('experimental-webgl');
if (!gl) {
alert('WebGL not supported, please use a different browser.');
}
// Vertex shader program
const vertexShaderSource = `
attribute vec4 aVertexPosition;
attribute vec4 aVertexColor;
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_Position = aVertexPosition;
vColor = aVertexColor;
}
`;
// Fragment shader program
const fragmentShaderSource = `
varying lowp vec4 vColor;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vColor;
}
`;
// Function to compile a shader
function loadShader(gl, type, source) {
const shader = gl.createShader(type);
gl.shaderSource(shader, source);
gl.compileShader(shader);
// Check if compiled successfully
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
const info = gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader);
gl.deleteShader(shader);
console.error('An error occurred compiling the shaders: ' + info);
return null;
}
return shader;
}
// Compile shaders
const vertexShader = loadShader(gl, gl.VERTEX_SHADER, vertexShaderSource);
const fragmentShader = loadShader(gl, gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER, fragmentShaderSource);
// Link the shaders into a program
const shaderProgram = gl.createProgram();
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check if linking was successful
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
console.error('Unable to initialize the shader program: ' + gl.getProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram));
}
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram);
// Get attribute locations
const vertexPosition = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aVertexPosition');
const vertexColor = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, 'aVertexColor');
// Define the triangle's vertices and colors
const vertices = new Float32Array([
// X, Y, Z, R, G, B, A
0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, // Top vertex (red)
-1.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, // Bottom left vertex (green)
1.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0 // Bottom right vertex (blue)
]);
const FSIZE = vertices.BYTES_PER_ELEMENT;
// Create a buffer and bind the vertices
const vertexBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer);
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices, gl.STATIC_DRAW);
// Enable the vertex positions
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
vertexPosition,
3, // Number of components per vertex position
gl.FLOAT, // Data type
false, // Normalize
FSIZE * 7, // Stride (7 floats per vertex)
0 // Offset
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vertexPosition);
// Enable the vertex colors
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
vertexColor,
4, // Number of components per color
gl.FLOAT, // Data type
false, // Normalize
FSIZE * 7, // Stride (7 floats per vertex)
FSIZE * 3 // Offset (skip first 3 floats for position)
);
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(vertexColor);
// Set the viewport to match the canvas size
function resizeCanvas() {
canvas.width = window.innerWidth;
canvas.height = window.innerHeight;
gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.drawingBufferWidth, gl.drawingBufferHeight);
}
// Initial resize
resizeCanvas();
// Resize the canvas when the window is resized
window.addEventListener('resize', resizeCanvas);
// Clear the canvas with a black color
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Draw the triangle
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
|
Check if all of the following conditions are true:
HTML Render
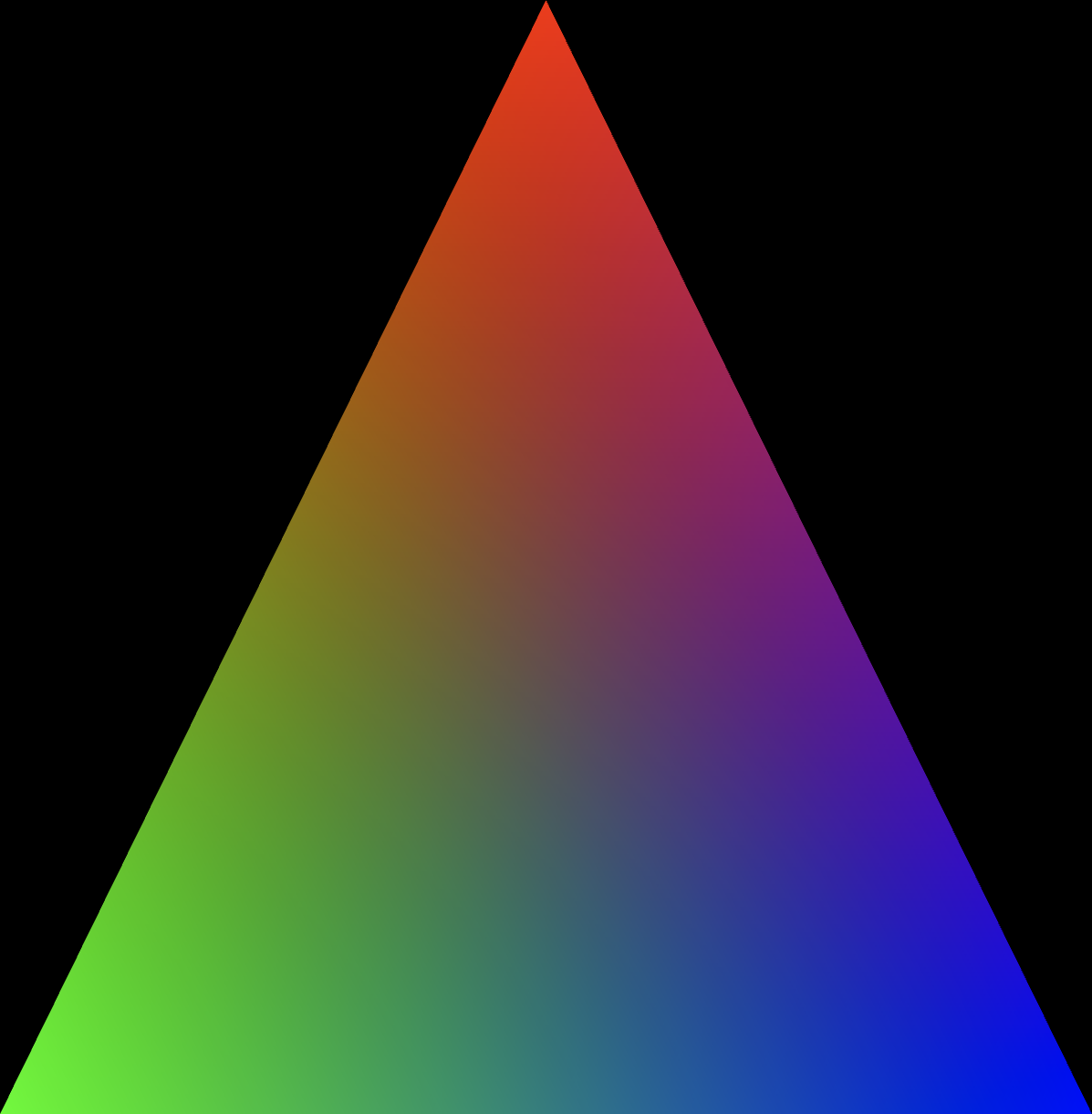
Rendering the webpage gives the following image:
LLM Generation
Query
This is a screenshot of a webpage that draws something with webgl. I'm trying to see if it drew what I wanted. Describe what is drawn in this image?
Output
The image shows a triangle with a gradient fill. The gradient transitions smoothly between several colors: red at the top, green at the bottom left, and blue at the bottom right. The background is black, which makes the colorful triangle stand out prominently.
LLM Generation
Query
Does this answer say that there is a picture of a triangle "The image shows a triangle with a gradient fill. The gradient transitions smoothly between several colors: red at the top, green at the bottom left, and blue at the bottom right. The background is black, which makes the colorful triangle stand out prominently."? Answer "Yes it does" or "No it does not".
Output
Yes it does.
Substring Evaluation
Testing if the previous output contains the string es it does: True
Check this condition is not true:
Substring Evaluation
Testing if the previous output contains the string THREE.: False
Final Answer: True
Final Answer: True

